The Revolution of Rapid Prototyping in Metal Fabrication
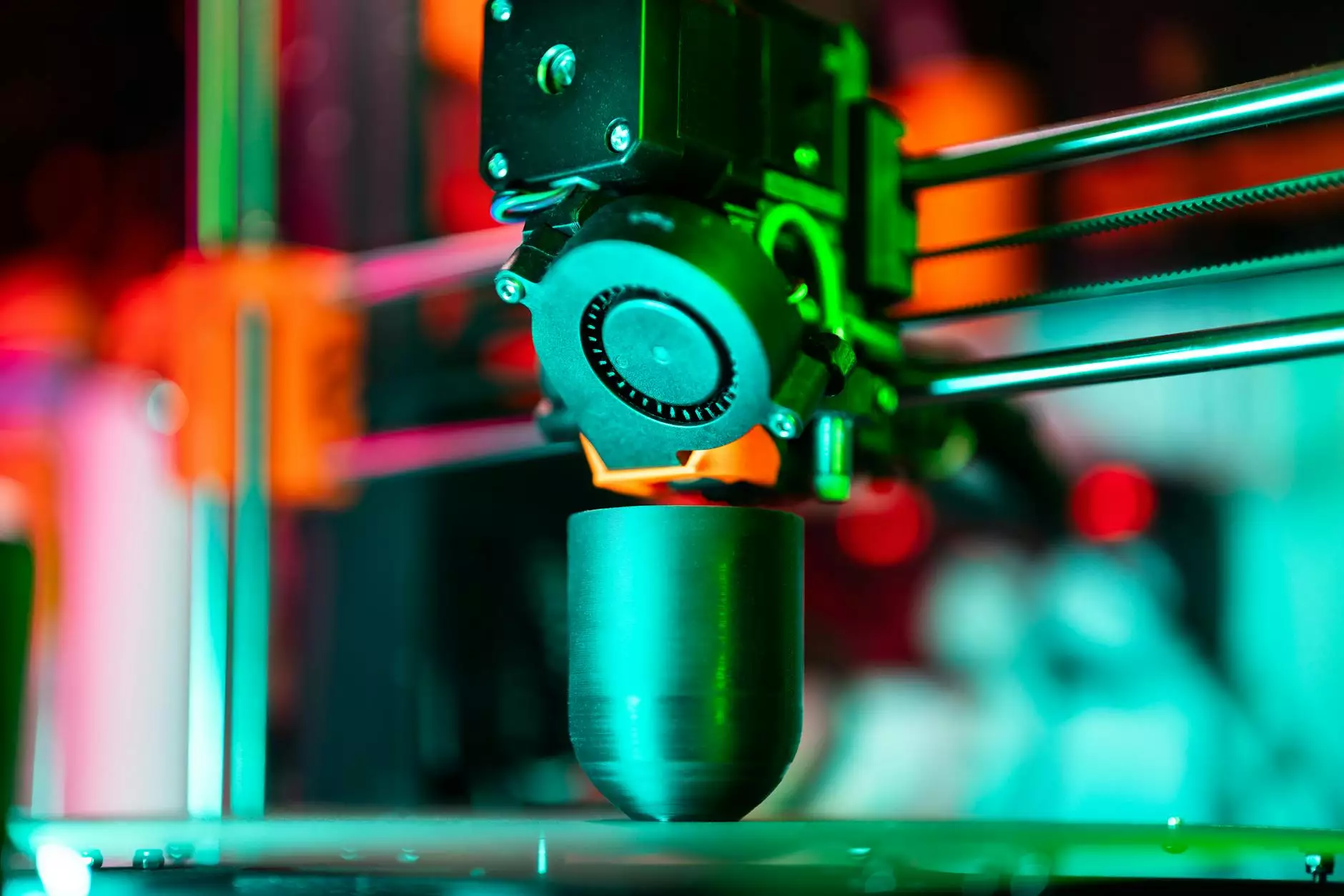

In the fast-paced world of modern manufacturing, the need for efficiency and innovation has never been more critical. Businesses are continuously seeking ways to improve their processes, reduce costs, and shorten lead times. One of the most significant advancements in this realm has been the development of rapid prototyping, especially within the context of metal fabrication. This article delves deep into the concept of rapid prototyping, its advantages, processes, and its impact on the industry.
Understanding Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is a suite of techniques used to quickly create a scale model of a physical part or assembly. It utilizes 3D computer-aided design (CAD) data, transforming it into a physical object swiftly and inexpensively. This innovative approach allows for the creation of prototypes that can be tested, modified, and iterated in a fraction of the time compared to traditional methods.
The Importance of Rapid Prototyping
In today's competitive landscape, getting products to market faster is crucial for success. The advantages of rapid prototyping in metal fabrication are manifold:
- Accelerated Product Development: Rapid prototyping significantly reduces the time from concept to production, enabling faster decision-making.
- Cost Efficiency: Early detection of design flaws can save significant costs by minimizing changes in later stages of production.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Rapid prototypes facilitate better communication among design teams, stakeholders, and clients, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
The Process of Rapid Prototyping in Metal Fabrication
The rapid prototyping process can be broken down into several key stages:
1. Design Conceptualization
The first step in any prototyping project is creating a detailed design. This is typically done using CAD software, which allows designers to craft intricate 3D models of the desired object.
2. 3D Printing and Manufacturing Techniques
Once the design is finalized, the next step involves employing various manufacturing techniques:
- 3D Printing: A popular technique that layers materials to create the object. Various materials can be used, including plastics and metals.
- CNC Machining: This method uses computer-controlled machines to remove material from a solid block (substrate), allowing for precise and complex geometries.
3. Testing and Evaluation
After manufacturing, prototypes undergo rigorous testing to validate functionality and design integrity. This feedback is crucial for making necessary adjustments before moving into full-scale production.
4. Iteration
Based on feedback from the testing phase, the design may go through multiple iterations, further refining and optimizing the product for the best performance.
Applications of Rapid Prototyping in Metal Fabrication
The applications of rapid prototyping in metal fabrication are expansive and versatile:
- Aerospace Industry: Rapid prototyping allows for the creation of lightweight, intricate components essential for aircraft design.
- Automotive Sector: The automotive industry benefits significantly from rapid prototyping in the development of parts and components, drastically reducing time-to-market.
- Medical Devices: In the healthcare field, rapid prototyping enables the swift creation of customized medical solutions tailored to individual patient needs.
- Consumer Products: Businesses can create and test new product designs rapidly, adapting to market demands effectively.
Benefits of Implementing Rapid Prototyping
Integrating rapid prototyping within a business not only streamlines operations but also enhances overall productivity. Here are some key benefits:
1. Boosts Innovation
With the ability to quickly transform ideas into tangible products, teams can explore innovative concepts without the fear of significant investment in time or resources.
2. Reduces Waste
By testing designs early in the development process, businesses can minimize material waste, thereby promoting sustainability and reducing costs associated with excess material.
3. Improves Quality
Rapid feedback and testing improve design quality, resulting in products that better meet customer expectations and regulatory standards.
Challenges of Rapid Prototyping
While there are numerous benefits to rapid prototyping, challenges still exist. Some common challenges include:
- Material Limitations: Not all materials are suitable for rapid prototyping, and limitations in material properties can affect the performance of the final product.
- Initial Setup Costs: The costs associated with setting up rapid prototyping equipment can be significant, making it more appealing for larger businesses with extensive budgets.
- Skill Requirements: Designing for rapid prototyping often requires specialized knowledge that may necessitate additional training for staff.
Future Trends in Rapid Prototyping
The landscape of rapid prototyping is continuously evolving. Here are some emerging trends that shape its future:
1. Advancements in Materials
The development of new materials will significantly impact the capabilities of rapid prototyping, with ongoing research focused on composite materials, metals, and biodegradable plastics.
2. Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Incorporating AI algorithms into the design process can enhance efficiency and introduce smarter ways to iterate on prototypes quickly.
3. Increased Automation
Advancements in robotics and automation technology are likely to lead to more automated rapid prototyping techniques, increasing speed, and reducing human error.
Choosing the Right Rapid Prototyping Partner
As businesses look to adopt rapid prototyping, selecting the right partner is critical. Here's what to consider:
- Expertise: Look for companies with a proven track record in rapid prototyping for metal fabrication.
- Technology: Ensure that your partner utilizes the latest technologies in 3D printing and CNC machining.
- Customer Support: A reliable partner will offer comprehensive support throughout the prototyping process, addressing any questions or concerns.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rapid prototyping stands as a transformative force in the field of metal fabrication, offering unparalleled speed, efficiency, and innovation for businesses across various sectors. By embracing this technology, manufacturers can not only enhance their product development processes but also stay ahead in an increasingly competitive market. As we look to the future, the significance of rapid prototyping will only grow, paving the way for advancements that can revolutionize industries and improve customer satisfaction.
For more information about advanced manufacturing techniques including rapid prototyping, visit deepmould.net.